Conversion Patterns of Agricultural Lands in Plains and Mountains: An Analysis of Underpinning Factors by Temporal Comparison with Geographically Weighted Regression in Depopulating Rural Japan
Authors
Yuki Sofue, Ryo Kohsaka*
Abstract
The significant decline and ageing of Japan's rural population has severely affected the maintenance of agriculture in these areas, resulting in the abandonment of agricultural land and subsequent conversion to other land use types. Dr. Yuki Sofue and Prof. Ryo Kohsaka quantified the change of land use in Matsusaka City, Mie Prefecture, located along the former Wakayama-kaido Road and in the Kushida River watershed, and analyzed the factors that can affect the change of agricultural land area using Geographically Weighted Regression analysis. Using this method, it is possible to estimate for each location the factors most associated with changes in agricultural land, such as elevation and the rate of population change. In most cities and villages, agricultural land area has decreased, suggesting that the rate of change and potential factors vary by geographical location, and that policies such as subsidy systems may also contribute. Most of the agricultural land converted in the plains was converted to residential land, while a high percentage of agricultural land in mountainous areas was converted to forest land or waste land. In addition, agricultural land in mountainous areas tended to be converted more often to agricultural land located at lower elevations than agricultural land located at higher elevations. This suggested that the subsidy system, such as the direct payment system, may make it easier to maintain agricultural land in mountainous areas that are subject to subsidies and to convert agricultural land in the boundary areas of mountainous areas that are not subject to subsidies.
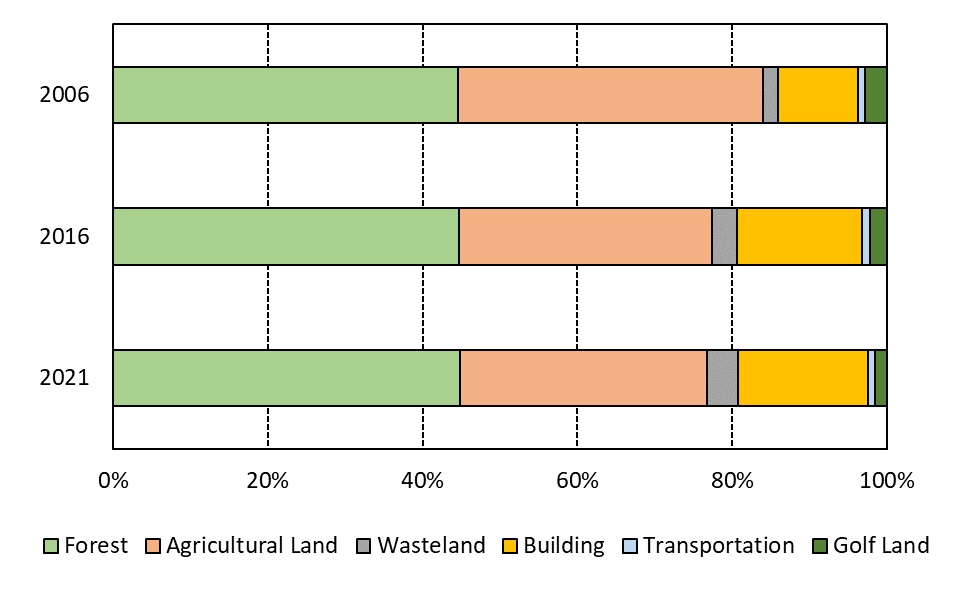
Figure 1. Changes in major land use ratios in Matsusaka City. Agricultural land decreased by 13.4%, while building land and waste land increased by 11.9% and 3.7%.
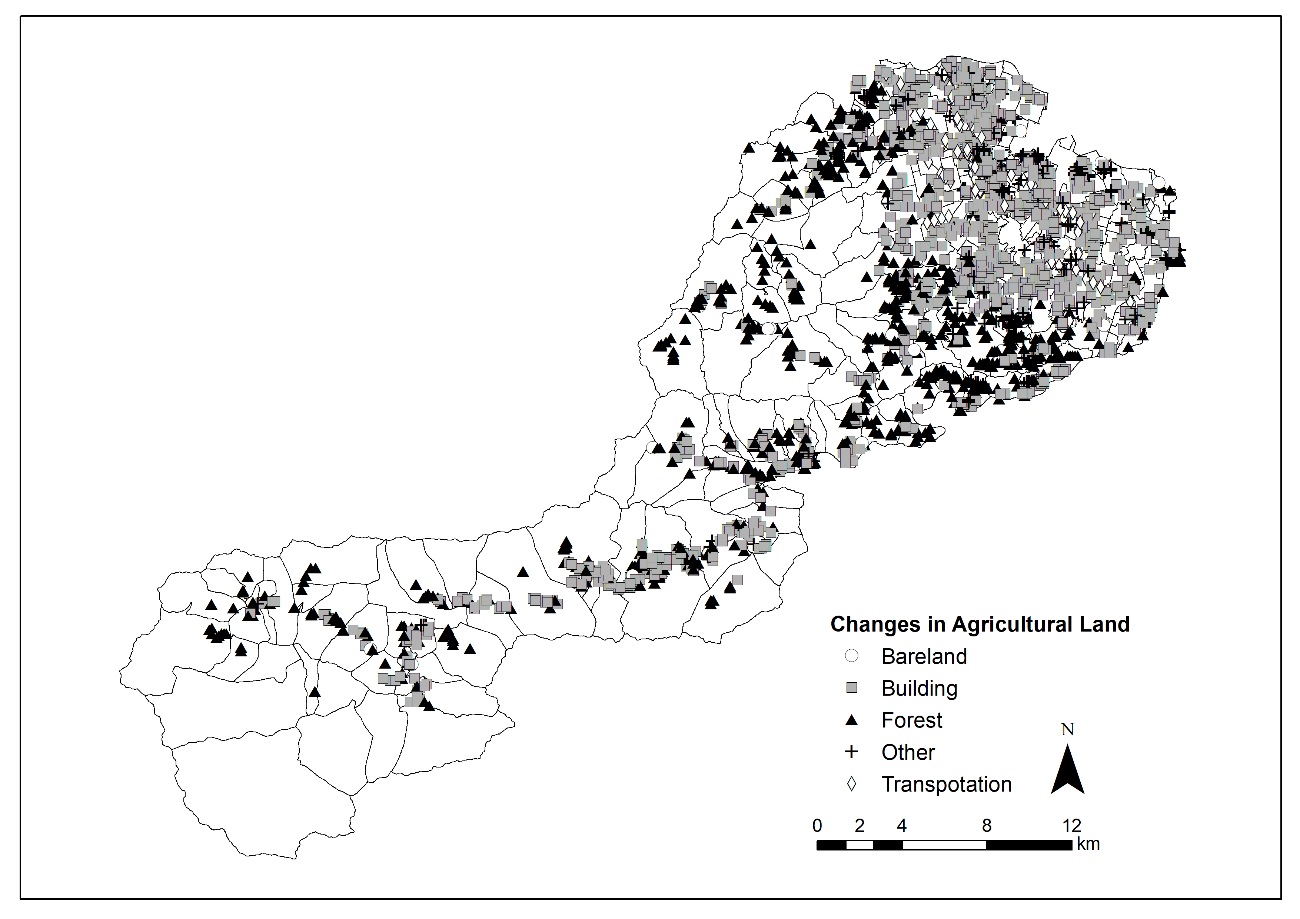
Changes in agricultural land. A map showing the destination of conversion from agricultural land. It can be seen that many agricultural lands in the plain (the eastern part of Matsusaka City) were converted to building sites, and many agricultural lands in the mountainous areas (the western part of Matsusaka City) were converted to forests and wasteland.
This study was conducted as a part of the scientific research and development program for the JST/RISTEX science and technology innovation policy "Development and practice of consensus formation method for promotion of policy compatible with agriculture and forestry production and environmental conservation"(https://www.jst.go.jp/ristex/stipolicy/project/project40.html). The results derived from the JSPS (JP23KK0198, JP23H01584, JP23H03605, JP22H03852, JP21K18456, and JP17K02105) carried out in the laboratory.
Paper Information
- Journal
- : Environmental and Sustainability Indicators
- DOI
- : 10.1016/j.indic.2024.100346

